Circuit Applications
Charge Pumps
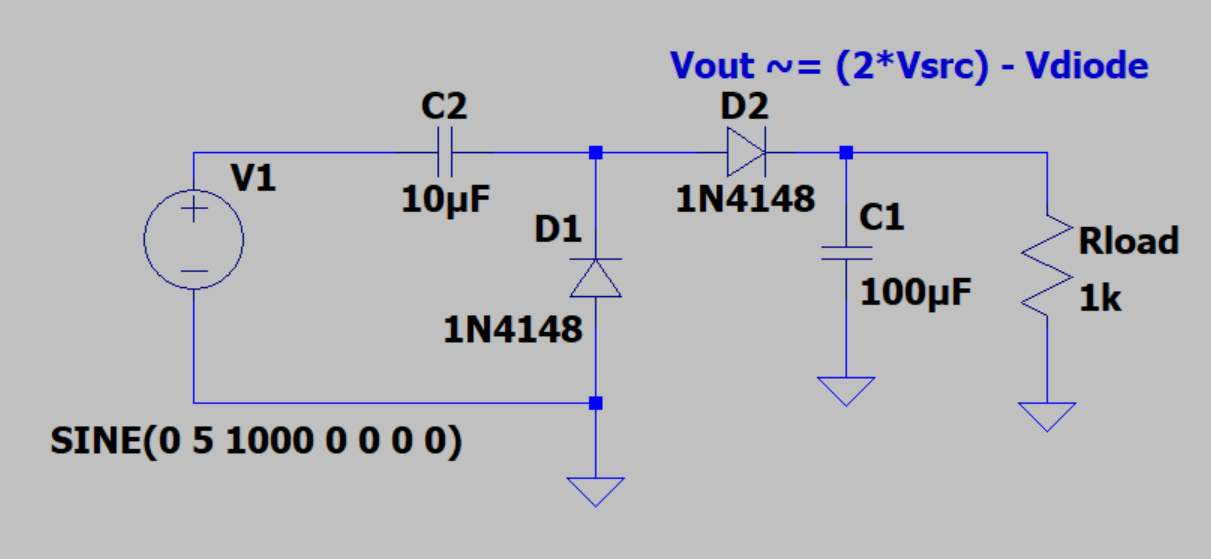
Positive voltage charge pump.
A charge pump is a circuit that uses a periodic signal and diodes to force charge buildup on a capacitor. While this is an effective way to store an energy potential, the voltage will approach the peak-to-peak voltage unless dissipated on a load or regulated. The size of the capacitors and the frequency of the input waveform will determine the time it takes for the circuit to charge.
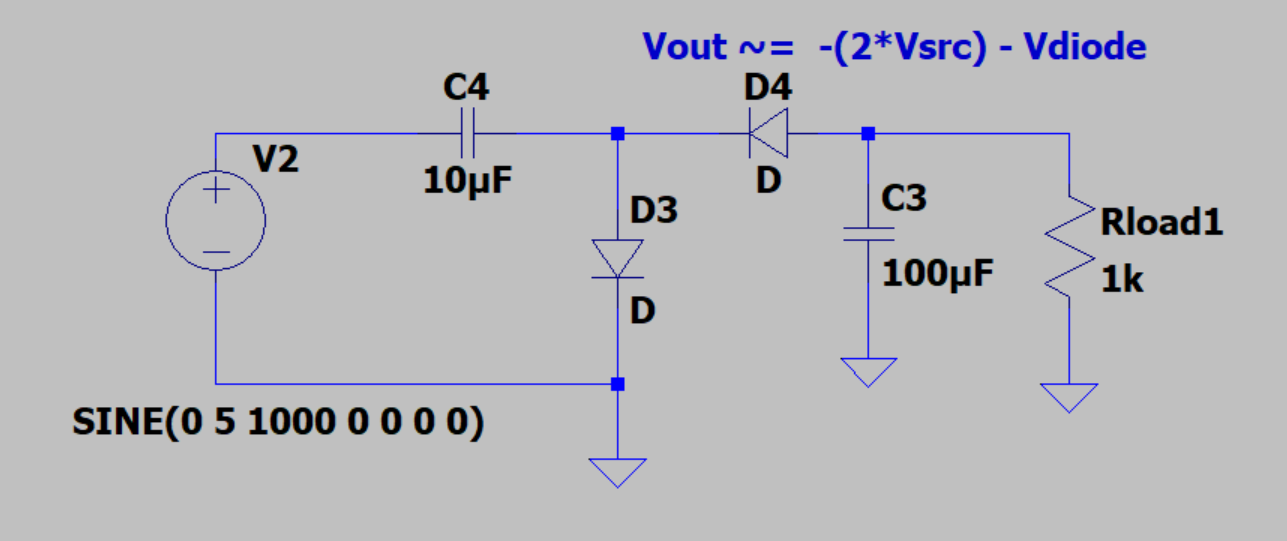
Negative voltage charge pump.
Negative voltage rails are often needed for reference voltages and are a useful addition to many circuit designs. An easy approach for low current applications could rely on a negative charge pump.
An H-bridge is a circuit configuration consisting of four transistors, primarily MOSFETs or BJTs configured in an H pattern. Each side of an H-bridge has a complementary set of transistors where only one transistor on each side is active at a given time. If two transistors on one side are on, a short circuit will occur as the attached transistor try and source and sink as much current as possible. During normal operation, current flows through an attached device in one of two directions.
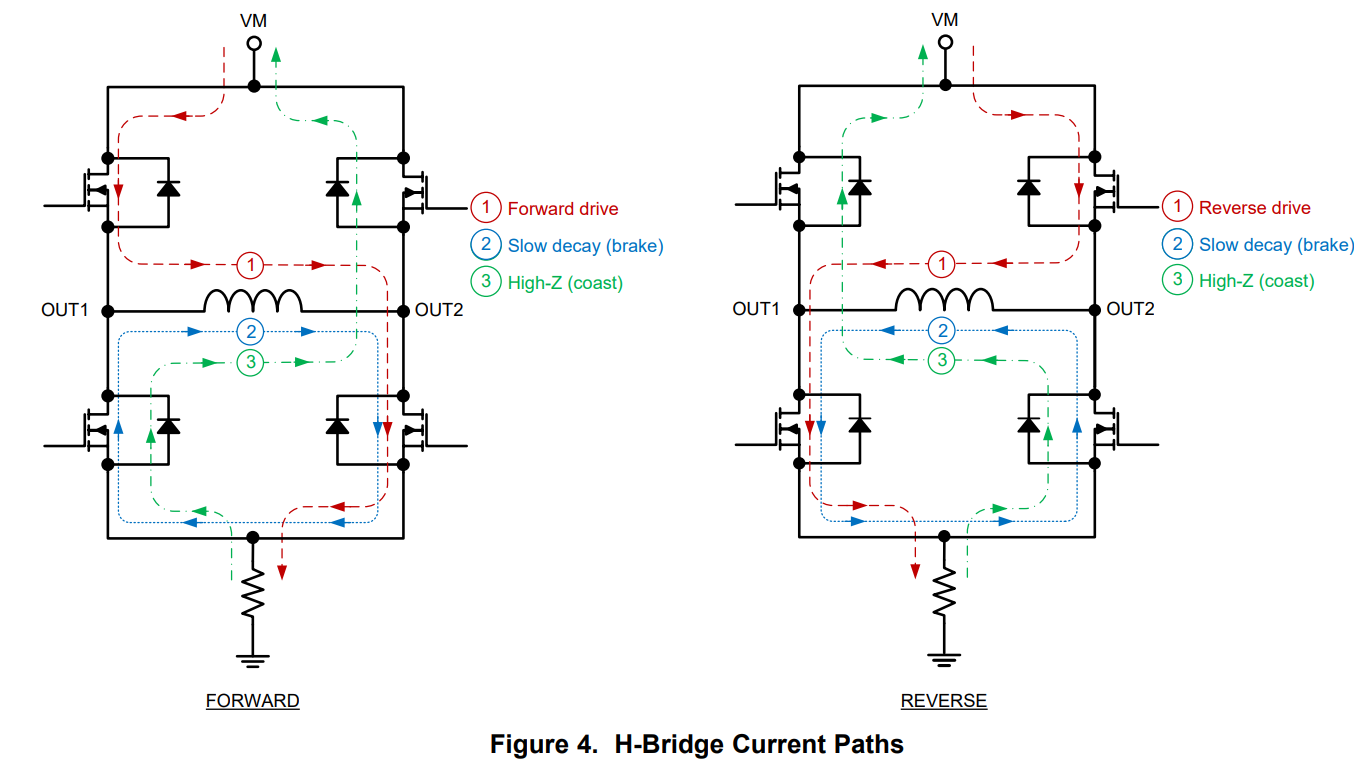
H-Bridge circuit and current paths [1].
The circuit essentially acts as an alternating set of switches so that the current flow or polarity may be swapped on a device. H-bridges are commonly used for motor drivers because of their ability to swap polarity, allowing forward and reverse motion control. Braking and coasting configurations are also available for abrupt or natural decaying stops respectively. H-Bridge circuits can be made discretely or be found in integrated packages often with driver circuitry included. Driver circuitry simplifies the process of controlling an H-bridge and insures safe operation. Often, H-bridge drivers only require static digital values or a PWM signal to change the average voltage and current applied.
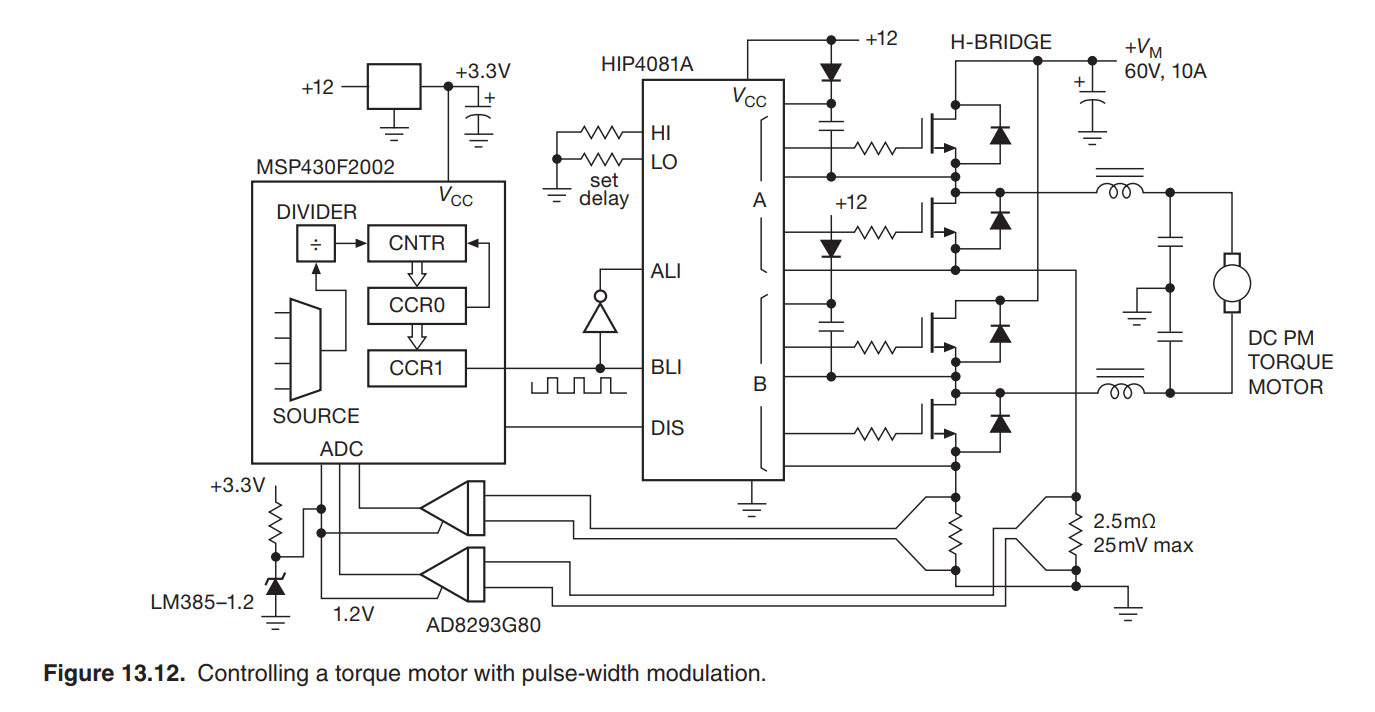
Discrete H-bridge driver solution [2].
References
- 1
Texas Instruments. “DRV8871 3.6-A Brushed DC Motor Driver with Internal Current.” [Online]. Available: [www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/drv8871.pdf].
- 2
Horowitz and W. Hill, “The Art of Electronics.” Cambridge University Press, 2022.